|
| Navigation<> |
Current studies:
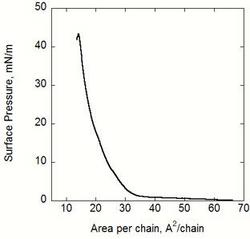
These classical techniques give information about the overall phase behaviour and the electrostatic properties of the monomolecular layer spread on the liquid surface.
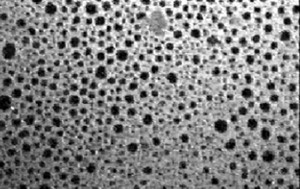 Fluorescence microscopy image from a DPPC monolayer doped with NBD-PC. The domain size is approximately 35 µm.
Fluorescence microscopy image from a DPPC monolayer doped with NBD-PC. The domain size is approximately 35 µm.
Fluorescence Microscopy can be used to visualise domain structures in lipid monomolecular layers formed on the water/air interface at different surface pressures, and to investigate the effects of various solutes such as ions and proteins in the aqueous subphase on domain structure. The domain structure of membrane lipids is believed to be important to the function. We use fluorescence microscopy to detect lipid domain formation and dynamics.
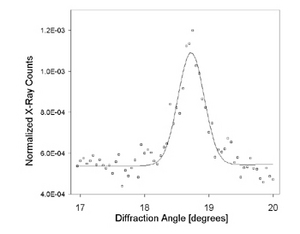
The 2D order in the monolayer can be resolved using GIXD. The methods gives valuable information about change in molecular ordering due to interactions with solutes such as skeletal proteins or changes in the surface pressure.
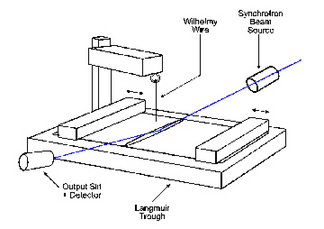
 One of our Langmuir troughs mounted in Station 16.2 at the Daresbury
Synchrotron Radiation Source.
One of our Langmuir troughs mounted in Station 16.2 at the Daresbury
Synchrotron Radiation Source.